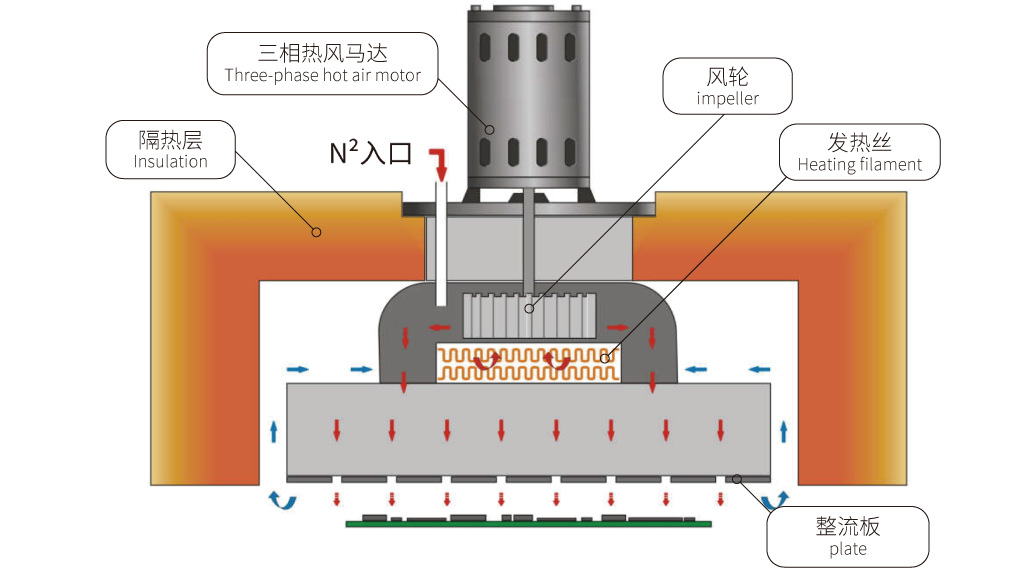
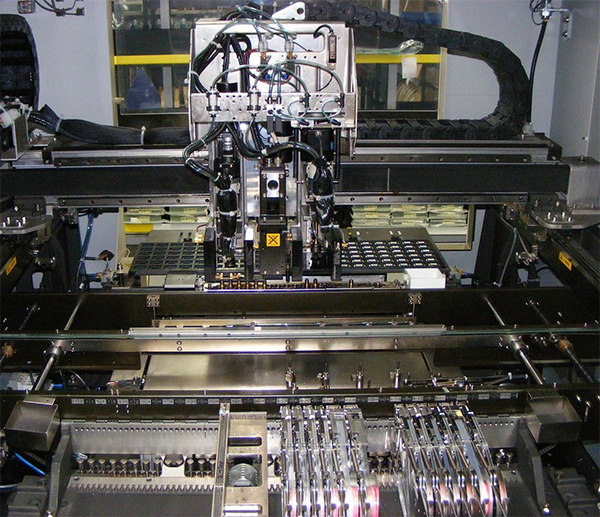
Why SMD and SMT are Important for Modern Electronics?
Electronics are at the heart of modern life, powering everything from smartphones to medical devices. But what makes this technology so efficient and compact? This is SMD and SMT come into play as these two terms define the foundation of modern circuit design. This has enabled devices to become smaller, faster, and more reliable.
What Does SMD Mean in Electronics?
Surface Mount Devices, or SMDs, are components that sit directly on the surface of a printed circuit board (PCB). Unlike traditional components, which require drilling holes for leads, SMDs use pads on the board for direct connection.
This design innovation allows for a higher density of components on smaller boards, paving the way for compact gadgets. SMDs include resistors, capacitors, diodes, and more, each tailored for surface mounting. Their rise in popularity aligns with the growing demand for miniaturization and cost-effective manufacturing.
Difference Between SMD and SMT
At first glance, SMD and SMT might seem interchangeable, but they represent different concepts in electronics. SMD refers to the physical components such as resistors, capacitors, ICs, and others that are mounted directly onto a PCB’s surface. SMT, on the other hand, is the technology or methodology used to place and secure these components.
Think of it this way: SMDs are the “actors,” while SMT is the “stage” and “script” that orchestrate their placement. SMT uses specialized machines and techniques to solder SMDs onto PCBs, ensuring precise alignment and functionality. Together, SMD and SMT revolutionized electronic manufacturing by making it faster and more reliable.
Applications of SMD and SMT in Electronics
SMD and SMT have found their way into almost every corner of the electronics industry. They are well-suited for a variety of applications.
- Consumer Electronics: Devices like smartphones, tablets, and laptops rely heavily on SMD and SMT for their compact designs and high performance.
- Automotive Industry: Modern vehicles use advanced electronics for navigation, safety, and entertainment, many of which incorporate SMT assembly.
- Medical Devices: Precision and reliability are paramount in medical electronics, where SMDs enable miniaturized and robust devices.
- Industrial Automation: SMT’s high-speed assembly process suits the demanding requirements of industrial control systems and robotics.
Advantages of Using SMD and SMT
SMD and SMT have redefined electronics manufacturing, offering numerous advantages over traditional through-hole methods:
- Miniaturization: SMDs allow for smaller, lighter designs, making them perfect for portable devices like smartphones and wearables.
- Cost Efficiency: The SMT process is largely automated, which minimizes labor expenses and shortens production times.
- Increased Functionality: By enabling high-density component placement, SMDs allow for more complex circuits on smaller boards.
- Improved Performance: The shorter lead lengths of SMDs reduce parasitic capacitance and inductance, enhancing circuit performance.
- Reliability: SMT assemblies are highly reliable under mechanical stress, making them ideal for automotive and industrial applications.
The evolution of SMD and SMT has transformed the way electronics are designed and manufactured. From compact consumer devices to robust industrial systems, their influence is undeniable. In fact, their combination of precision and efficiency strongly implies they’ll remain an essential part of future technologies.